What is a Data Center?
Data centers are physical locations containing computer servers that store digital data.
Data centers guarantee business continuity in the event of a major incident: fire, flood, theft, intrusion, power failure or blackout.
A data center is a set of :
- a technical infrastructure covering the building and the energy/air-conditioning environment;
- an IT infrastructure grouping together the physical resources needed to host IS systems (transport, storage, data processing and security).
Data center premises
|
Premises |
Function |
| Server rooms | Receive the technical resources needed to host IS. |
| Network premises | Contain the data center network core. Depending on the configuration of the datacenter, the network equipment can be integrated into server rooms. |
| Telecom premises | Contain arrivals from the extended network. |
| Stock area | Store unused equipment. Inventories provide a degree of flexibility in the management of the and ensure operational continuity. |
| Preparation | Prepare equipment for installation in server rooms. It’s a workspace that also to disassemble, modify, test or recondition any data center equipment. |
| Offices | Host the data center management team. Depending on requirements, they could be temporarily used by customers or external service providers as part of a project, for example. |
Reminder of data center configuration ![]()
Logistics or tertiary zone
- Personal welcome
- Material delivery and storage
- Operations team offices
Computer zone
- Computer rooms
- Network and/or operator premises
Technical area
-
Electrical rooms
-
Air-conditioning/ventilation rooms Safety/security rooms
-
Often outdoors, production equipment requiring heat exchange heat exchange (chillers, generators, etc.)
Global architecture of a data center
The contents of a data center
 The perimeter
The perimeter
- The land and its surroundings.
- A safe shell: The building.
- Interior architecture adapted to the operation.
- Heavy and complex technical installations.
- Real-time supervision.
High-performance site management.
Heavy and complex technical installations
High-performance electrical installation adapted to the activity
- Electricity supply
- Power & lighting distribution
- Electrical protection (overvoltage, lightning protection, thunder protection, earthing systems, etc.)
- Generators (internal production of electrical energy)
- Inverters/batteries (high-quality power for IT equipment)
Air-conditioning and ventilation systems adapted to the activity
- Cold production
- Cold distribution
- Air-conditioning terminals for IT and technical rooms
- Air handling unit to supply the data center with fresh, treated air.
- Fresh air distribution and extraction.
Efficient fire safety system adapted to the activity
- Fast, highly sensitive fire detection system.
- Fire extinguishing system not harmful to IT equipment.
Water and fluid leak detection system
- Sensitive installation for early detection of water and fluid leaks.
- Drainage system in case of leaks.
Access control and video surveillance systems
- Access control for each room and zone (badge, biometrics, etc.)
- Anti-intrusion protection
- Video surveillance
Monitoring and supervision
- Centralized technical management to supervise and control the smooth running of the entire technical installation.
- Report alarms and incidents in technical installations.
Pre-cabling adapted to data center requirements and standards
Data center specifications
A data center must be designed to ensure :
- High availability of electricity, climate control and telecommunications.
- High fire safety
- A high level of physical security
- Optimum control of electrical energy.
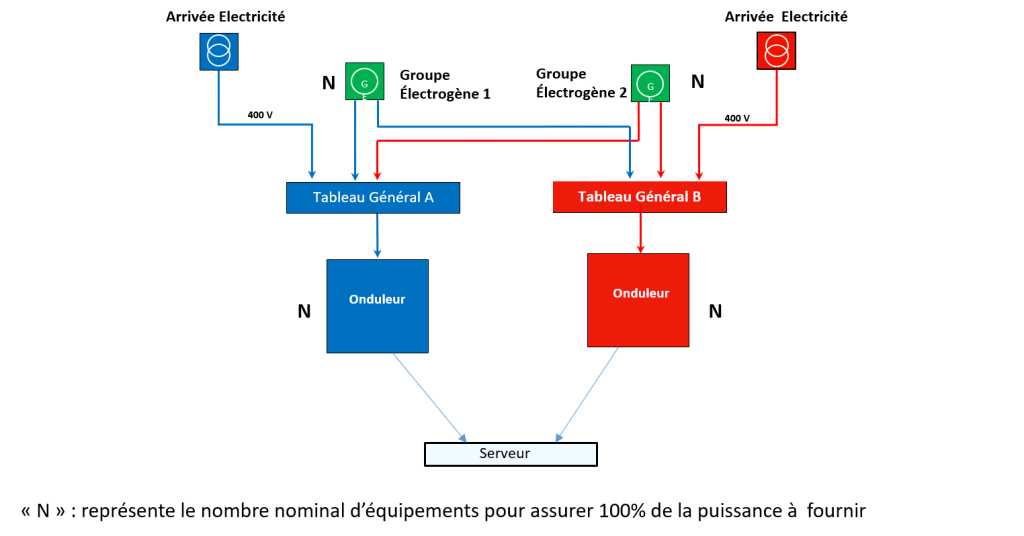
Notion of redundancy
To ensure high infrastructure availability and service continuity, we deploy a modular, efficient architecture for technical equipment.
-
No power cuts (24/7)
-
Maintain a given temperature in the computer room (24h – 7d/7)
Resources : Double (redundant) equipment and distribution.
High-quality energy (inverters)
To ensure high-quality power for IT equipment, we deploy a secure, uninterruptible power supply. Inverters are used to stabilize voltage, protect against and compensate for micro-interruptions.
Inverter type
Online with double conversion
is best suited to data centers.
Generators
A data center must have its own internal energy production, independently of electricity suppliers. Requirements must be met in terms of unit redundancy, power, continuous operation and fuel autonomy.
The generators must ensure that the data center is fully supplied with electricity in the event of a power cut from external suppliers, either for a micro outage or an extended outage of up to 72 hours.
NB: according to standards, generators are considered to be the data center’s main source of energy. Energy from external suppliers is only an economical alternative.
Fire safety
- A data center must have a fire safety system that is efficient, early, fast-acting and non-harmful.
- The fire safety system must detect the start of fires at an early stage (hyper-sensitive smoke detection).
- VESDA (Very Early Smoke Detection) detectors are recommended.
- The extinguishing system must be triggered quickly to smother fire starts, using an extinguishing agent that is not harmful to IT equipment.
- Inert gases are adapted to the activity.
- Avoid gases that are harmful to equipment, such as synthetic gases.
Physical security
An important aspect of data center design and operation is physical security, which is an important criterion for data center customers.
- The data center must be highly secure, with an effective access control system. From the external fence onwards, each area of the data center needs to be protected, and each room needs to have increasingly higher levels of access, depending on its criticality.
- A video surveillance system is required. Also an anti-intrusion system.
- A central access control and security station (PCS) must be set up to monitor the data center 24/7 with qualified security guards.
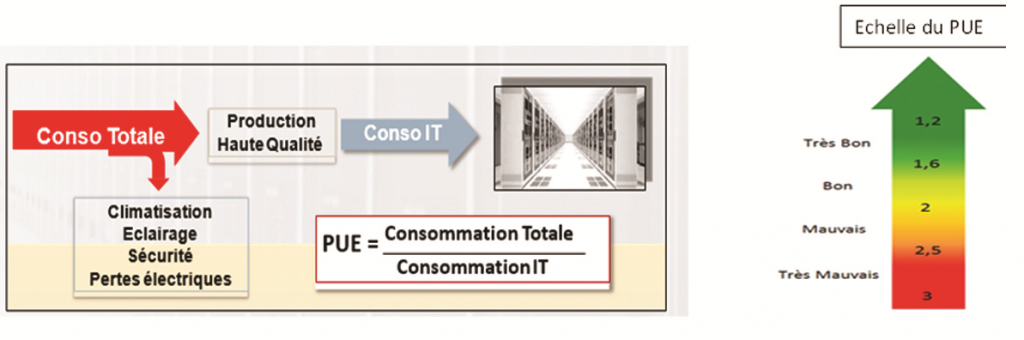
Energy performance
The most important factor in data center reliability is energy efficiency.
Planning, design and operation must take into account the data center’s energy performance and optimal energy consumption.
The most telling ratio in this area is the
PUE (Power Usage Effectiveness).
- Measures the data center’s energy performance on the basis of electricity consumption readings (kWh) over 1 year.
- This is the total consumption of the data center divided by the net consumption of IT equipment.